In this short thought experiment, I try to outline possible first steps how you can recover from a disaster described as follows. It is partly based on a real-world scenario I was told about at a VMUG meeting.
Suppose you lose your whole VMware environment due to an HBA going mad.
It arbitrary overwrites files on your VMFS LUNs and destroys all virtual machines. Your critical infrastructure as Domain Controller, application server, database server and even your Veeam Backup & Replication server are down…
In the worst case, you have no idea which host is causing the failure and you have to install some VMware hosts from scratch on replacement hardware, too.
All that remains are the Veeam repositories with the backup files. By the way, this can also happen in a similar way due to a ransomware attack…
Do you have a plan for a scenario like this?
There are various ways to recover your Veeam B&R server and production, depending on the available resources (staff, replacement hardware, time, backup data center…) and technologies (eg. Instant Recovery).
Some possibilities are sketched in the following consideration.
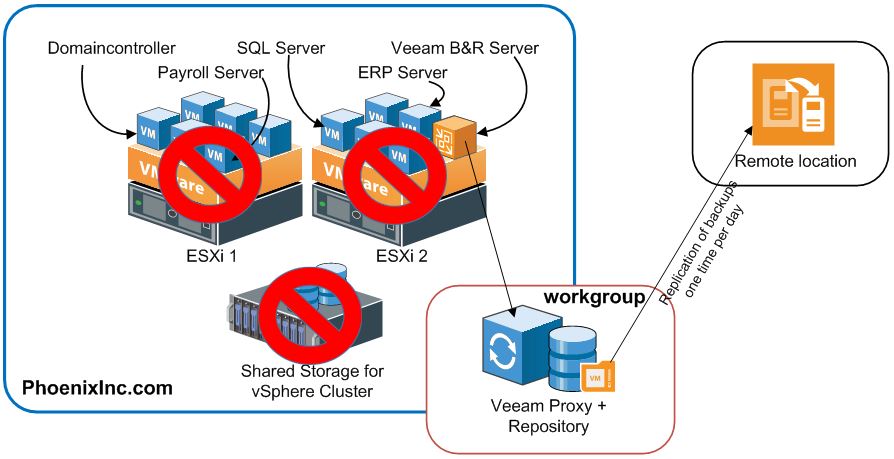
Let’s take a look at the environment when everything is working as expected:
![Disaster Recovery consideration example]()
All servers of our sample company Phoenix Inc. are virtualized running on a small VMware vSphere Cluster. Some VMs are providing infrastructure services like AD, DNS and DHCP. Others are hosting database services and applications.
The Veeam Backup & Replication server is virtualized, too writing the backups to a physical repository server with local disk storage. For disaster recovery, all backups are replicated to a remote location.
This is a setup that you can find in many SMB sized companies…
The fun begins, when the picture changes to something like this…
![Disaster Recovery all down]()
Let’s stick to the failure scenario described in the beginning of this blog post.
An HBA in one of the VMware hosts went mad due to a (fortunately rare) failure situation and wiped-out all your VMFS datastores. As a consequence, all VMs are destroyed and nobody can work anymore, as critical services as Active Directory and DNS are down, too.
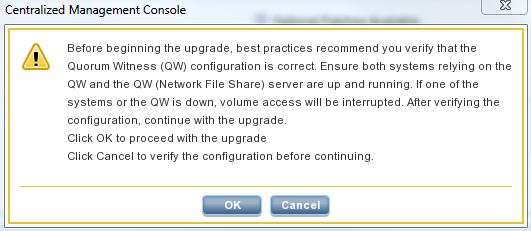
Unfortunately, there is no chance to use magic features like Veeam’s Instant Recovery, as the Veeam B&R Server is among the victims.
So it is time to draw up a plan how to bring the systems up and running as fast as possible…
The next moves should be…
- install VMware vSphere ESXi on a new hardware and provide access to storage (shared storage or local disks)
- Recover your Veeam B&R server
- bring back the most important infrastructure services like Active Directory, DNS and DHCP asap
- restore all other VMs depending on their RTO (recovery time objective) classification
The first task should be realized relatively easily, provided that there is replacement hardware available. All you need is a hypervisor with access to local storage/shared storage, where you can restore your VMs and a network connection.
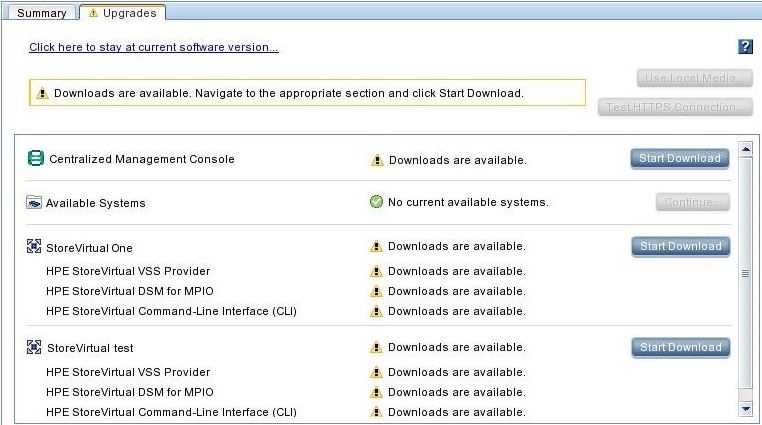
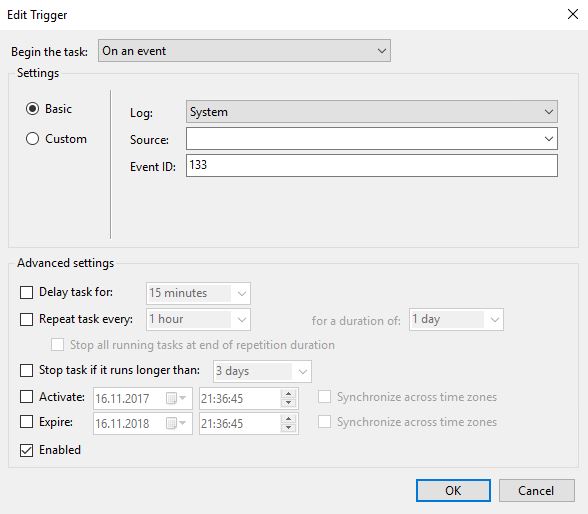
Task two is definitely a bigger challenge. Typically you are used to relying on the Veeam Console to restore VMs, databases, and files…
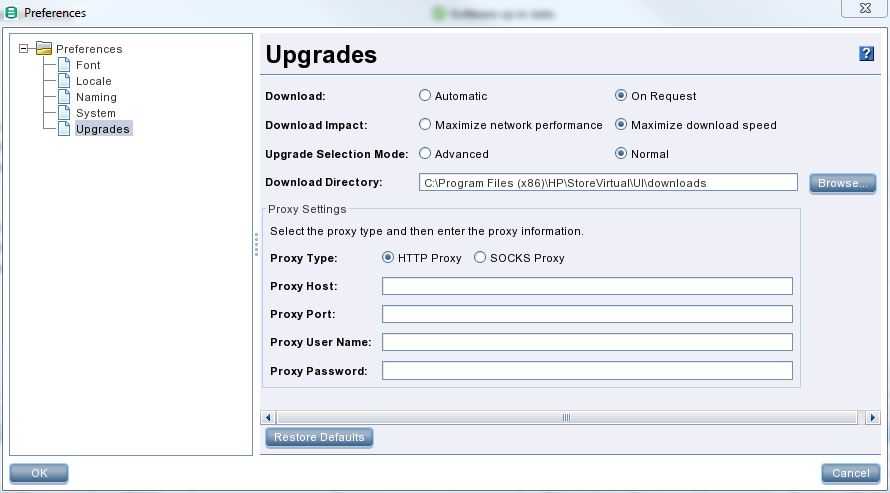
Ways to restore a Veeam B&R Server:
(p) is valid for a physical installation (v) for a virtual installation
Depending on your design/DR preparations you can choose between the following possibilities to restore your Veeam B&R Server:
Replication of the VBR Server to a remote location is in place? (v)
- Start replica in the remote location manually (no need to reinstall Veeam B&R)
Veeam Server Configuration Backup is available? (v) (p)
Veeam backup files of your Veeam B&R Server are available (.vbk file) (v)
Absolutely no Veeam B&R server backups are available
No panic! You still have some possibilities left to survive:
- (v)(p) Install a new Veeam B&R Server from scratch and import the backups files from the surviving repositories. Without any backup of your Veeam server you have of course lost all your settings and configurations. This is annoying, but you can fix it after you have handled the disaster. For now, you can restore your production!
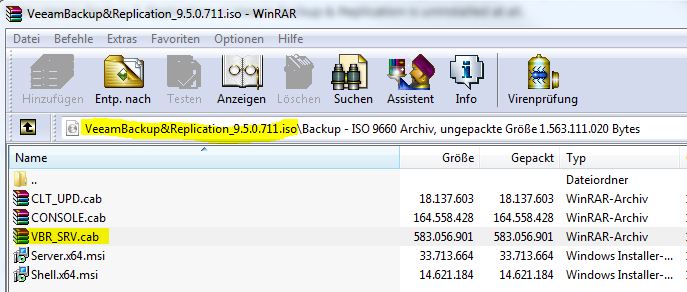
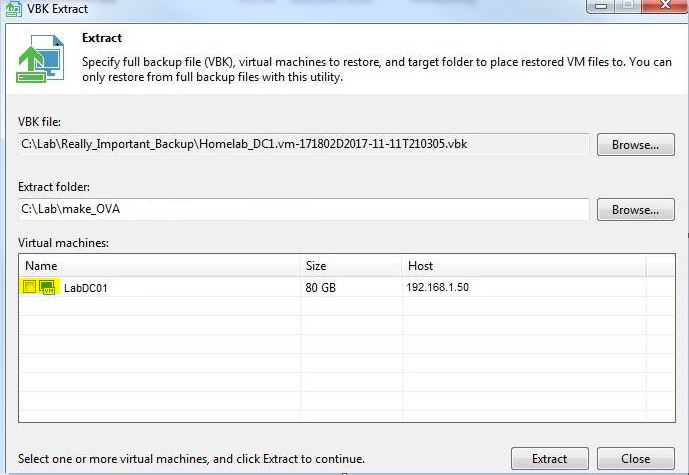
- (v) Use the Extract Utility to restore VMs without having a Veeam Installation in place and re-add them to your VMware inventory. (Veeam Extract Utility)
After a successful recovery of your Veeam B&R environment, you can start to restore your VMs depending on their RTO (recovery time objective) classification.
And soon our sample company looks again like this (hopefully): ![🙂]()
![Disaster Recovery consideration example]()
Short and Sweet
There are numerous possibilities to recover a Veeam Backup and Replication Server after a disaster. And as long as you have functional, current backup files available, you can even restore them without any Veeam installation.
Nevertheless, it is necessary to prepare for the different disaster scenarios and test the recovery procedures regularly.
“By failing to prepare, you are preparing to fail” (Benjamin Franklin)
Do you have better/more/other suggestions to handle this disaster? Is something wrong? Just leave a comment!
Der Beitrag Consideration: All systems down! Recover your Veeam Backup & Replication server erschien zuerst auf All about virtualization.





















 Forever Forward Incremental:
Forever Forward Incremental:
 Reverse Incremental Backup:
Reverse Incremental Backup: